Answer
Oct 31, 2024 - 06:35 AM
A Class D audio amplifier works by converting the input audio signal into a series of high-frequency pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals, which effectively switch the output transistors on and off. This rapid switching allows the amplifier to efficiently transfer power to the speaker with minimal heat loss. The PWM signals are then filtered to remove high-frequency components, leaving the amplified audio signal.
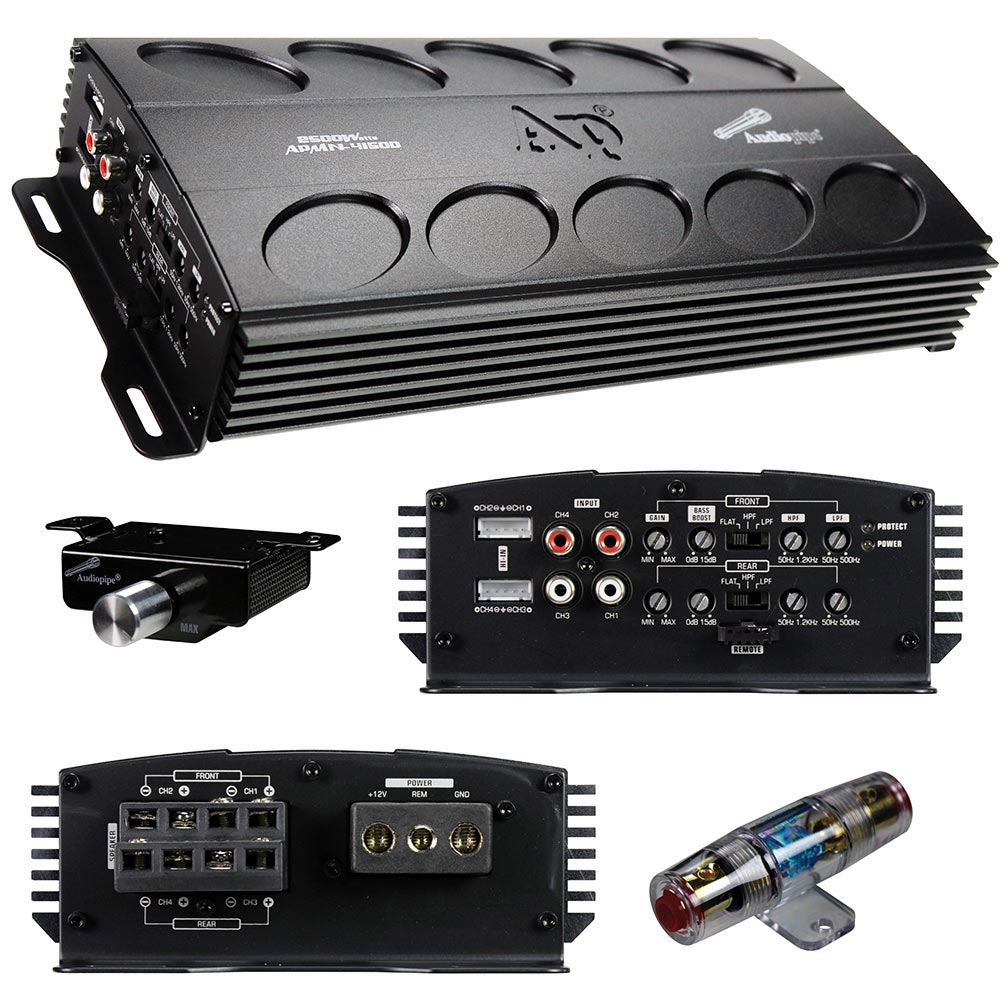




Add New Comment