Answer
Sep 13, 2024 - 06:55 AM
A Class A amplifier operates with its output transistors always on, delivering high linearity and audio fidelity but with lower efficiency and higher heat dissipation. In contrast, a Class D amplifier uses pulse-width modulation to switch its output transistors on and off rapidly, resulting in much higher efficiency and lower heat production, though it may introduce more distortion compared to Class A.
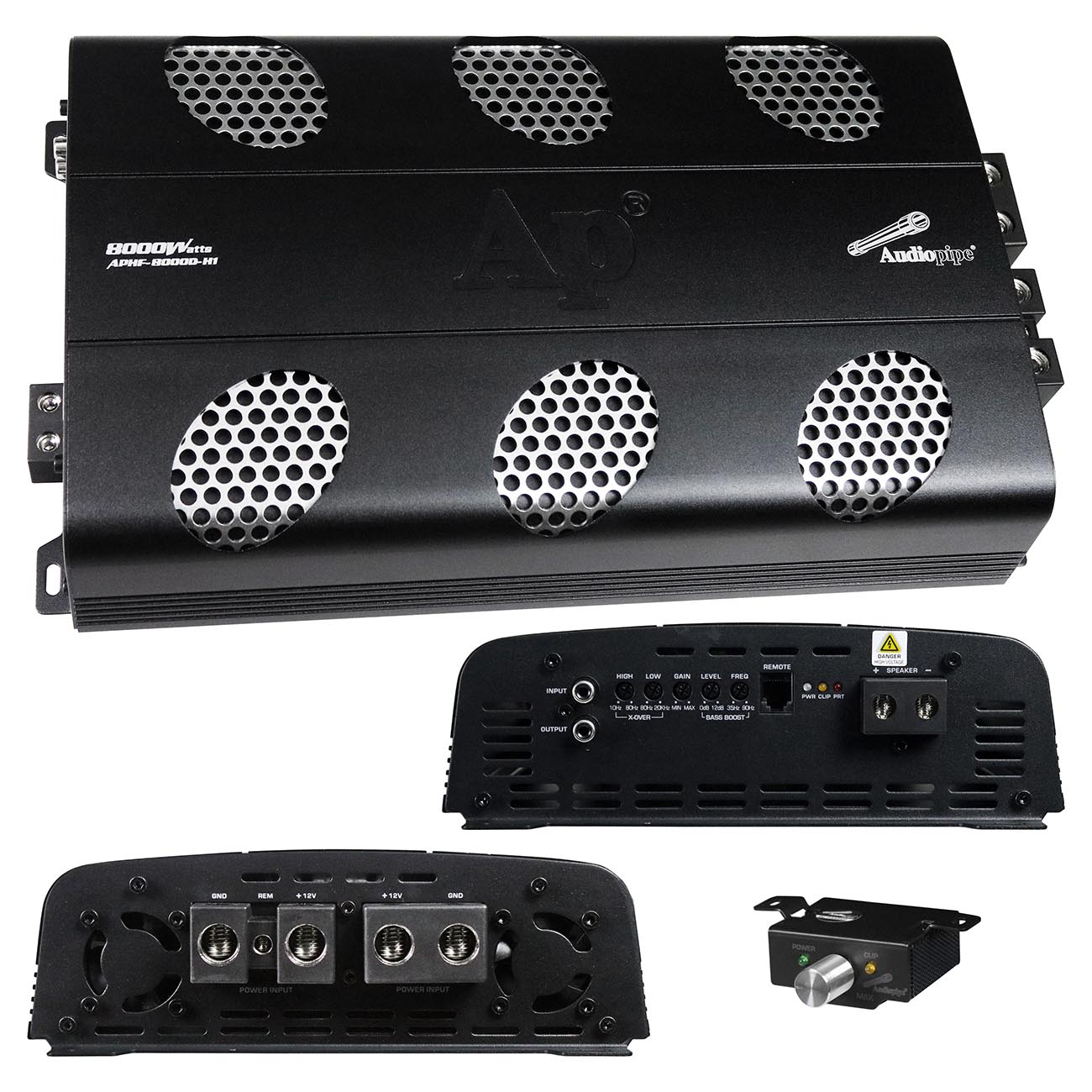
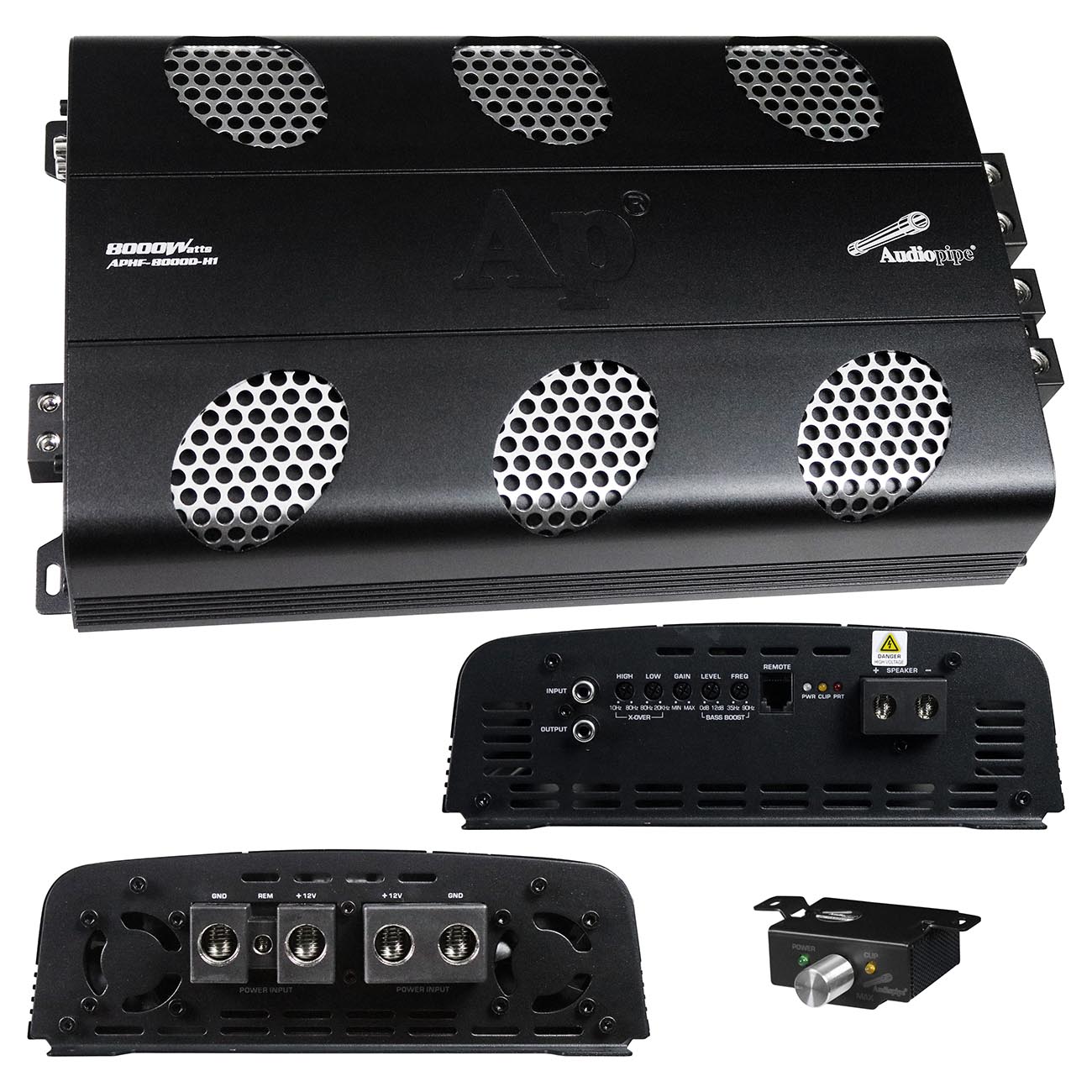




Add New Comment