Answer
Sep 09, 2024 - 11:06 AM
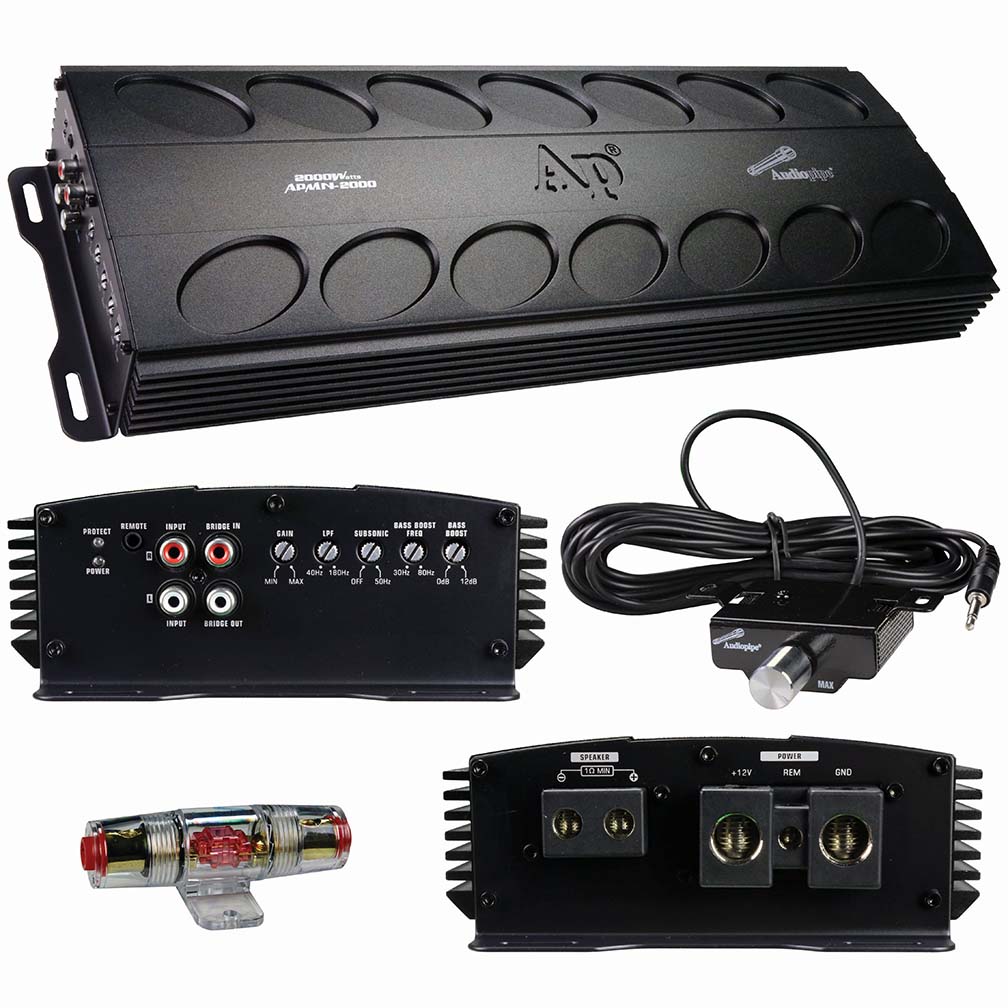
A Class D audio amplifier works by converting the input audio signal into a series of high-frequency pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals, which are then used to switch the output transistors on and off rapidly. These PWM signals are filtered through a low-pass filter to remove the high-frequency components, leaving behind a smooth analog audio signal that drives the speakers efficiently with minimal heat dissipation.




Add New Comment