Answer
Aug 28, 2024 - 04:18 PM
An audio power amplifier and a radio power amplifier serve different functions in electronic systems, and their differences become more pronounced when considering specific products like the Audiopipe APCLE-18001D, which is an audio power amplifier. Here’s a breakdown of what sets an audio power amplifier apart from a radio power amplifier:
1. Purpose and Application:-
Audio Power Amplifier:
- Purpose: The primary function of an audio power amplifier, such as the Audiopipe APCLE-18001D, is to amplify low-level audio signals (typically from a preamplifier, audio receiver, or head unit) to a level that can drive speakers or subwoofers. It boosts the signal's power to ensure that it can produce sufficient volume and sound quality for playback in a car audio system.
- Application: Used in car audio systems, home audio systems, and professional sound reinforcement systems to enhance the audio output. It is designed specifically to amplify audio frequencies (typically from 20 Hz to 20 kHz) to create a full-range sound or enhance bass frequencies for subwoofers.
-
Radio Power Amplifier:
- Purpose: A radio power amplifier is designed to amplify RF (radio frequency) signals for transmission. It takes a low-power RF signal from a radio transmitter and amplifies it to a higher power level to increase the transmission range or signal strength.
- Application: Commonly used in communication systems, such as radio broadcasting, amateur radio, cellular base stations, and military communication systems. It operates in a different frequency range (from a few MHz to several GHz) than audio amplifiers and is optimized for RF signals rather than audio signals.
-
Audio Power Amplifier (Audiopipe APCLE-18001D):
- Designed to amplify audio frequencies ranging from about 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which is the typical range of human hearing. The focus is on maintaining sound quality and fidelity across this frequency range, especially for bass, midrange, and treble sounds.
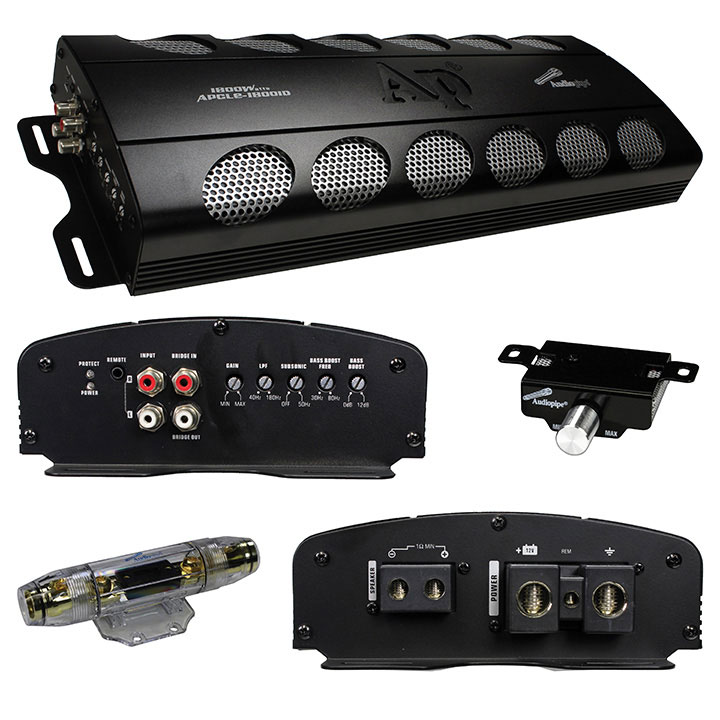
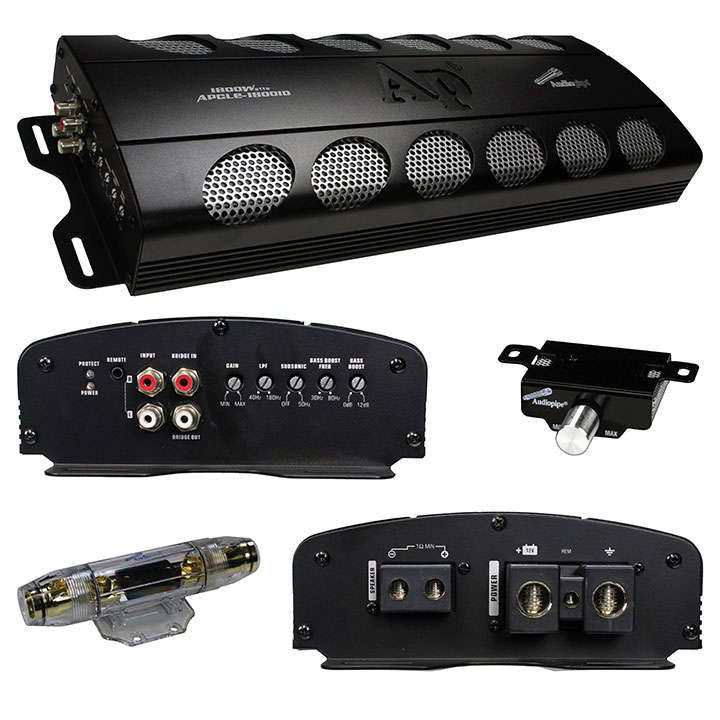
- The Audiopipe APCLE-18001D, in particular, is a monoblock amplifier often used to drive subwoofers, so it is optimized to handle low-frequency sounds (bass) effectively.
-
Radio Power Amplifier:
- Operates in the radio frequency (RF) range, which can be anywhere from a few megahertz (MHz) to several gigahertz (GHz). These amplifiers are designed to boost RF signals for transmission over long distances and are not concerned with maintaining audio fidelity.
-
Audio Power Amplifier:
- Typically designed with components that optimize the amplification of audio signals, such as transistors, capacitors, inductors, and resistors tailored to handle low to moderate frequencies with high fidelity.
- Features like low-pass filters, high-pass filters, and equalization controls may be included to allow users to fine-tune the audio output for better sound quality.
- The Audiopipe APCLE-18001D uses Class D amplifier technology, which is efficient for driving subwoofers due to its ability to produce high power with minimal heat generation.
-
Radio Power Amplifier:
- Designed with components that can handle RF signals, such as RF transistors, inductors, and capacitors that operate effectively at high frequencies.
- May include features like impedance matching networks and tuned circuits to ensure efficient transmission of RF signals with minimal loss or distortion.
- Emphasis is placed on maximizing signal strength and minimizing distortion in the RF range rather than focusing on audio fidelity.
-
Audio Power Amplifier:
- The output is tailored to match the impedance and power handling capabilities of speakers or subwoofers. For example, the Audiopipe APCLE-18001D provides high power output (e.g., 1800 watts RMS at 1 ohm) suitable for driving subwoofers to produce strong, clean bass.
- Efficiency and thermal management are crucial, especially in high-power amplifiers like the APCLE-18001D. Class D amplifiers are popular in car audio applications due to their high efficiency (up to 90% or more), which reduces heat dissipation and power consumption.
-
Radio Power Amplifier:
- Output power levels are measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW) and are often much higher than audio amplifiers to ensure effective transmission over long distances or through obstacles.
- Efficiency is also critical, but the focus is on maximizing the RF signal's strength with minimal loss rather than managing audio quality or fidelity.
-
Audio Power Amplifier:
- End users include car audio enthusiasts, home audio users, and professionals in live sound and studio settings who seek to enhance their audio experience with powerful, clear, and controlled sound reproduction.
- The Audiopipe APCLE-18001D, for example, is designed to deliver high power to subwoofers, enhancing the bass response in car audio systems.
-
Radio Power Amplifier:
- End users include radio broadcasters, communication professionals, amateur radio operators, and military personnel who need to transmit radio signals over long distances or improve signal strength and clarity.
- The focus is on reliable signal transmission and reception rather than audio quality.
The primary difference between an audio power amplifier like the Audiopipe APCLE-18001D and a radio power amplifier lies in their intended use, frequency range, design, and the types of signals they amplify. The Audiopipe APCLE-18001D is specifically designed to amplify audio signals within the human hearing range, providing high power output for car audio systems to enhance sound quality, especially for subwoofers. In contrast, a radio power amplifier is used for amplifying RF signals for communication purposes, focusing on transmitting radio waves over long distances rather than producing high-fidelity audio.




Add New Comment