Answer
Aug 13, 2024 - 03:07 PM
A full bridge Class D amplifier is a type of Class D amplifier that uses a full-bridge (or H-bridge) configuration to drive the load, typically a speaker. This configuration involves four switching transistors arranged in a bridge circuit, allowing the amplifier to deliver a higher output voltage to the load compared to a half-bridge design.
Key Features of a Full Bridge Class D Amplifier:-
H-Bridge Configuration:
- The full bridge amplifier uses two half-bridge circuits to form an H-bridge. This allows the output to swing between the positive and negative supply rails, effectively doubling the voltage swing across the load (speaker) compared to a single-ended or half-bridge amplifier.
-
Increased Power Output:
- Because the full bridge design can apply the full supply voltage across the load, it can deliver more power to the speaker compared to a half-bridge design. This makes full bridge Class D amplifiers ideal for high-power applications, such as driving subwoofers or other high-power speakers.
-
Efficiency:
- Like other Class D amplifiers, full bridge designs are highly efficient, converting a large percentage of the input power into output power with minimal heat loss. This makes them suitable for applications where power efficiency and heat management are critical.
-
Reduced Distortion:
- The full bridge design helps to minimize distortion by better balancing the output signal, which is important for maintaining sound quality, especially at higher power levels.
-
Speaker Protection:
- The symmetrical nature of the full bridge design can offer better protection to the speaker by providing a balanced load and reducing the risk of DC offset, which can damage speakers.
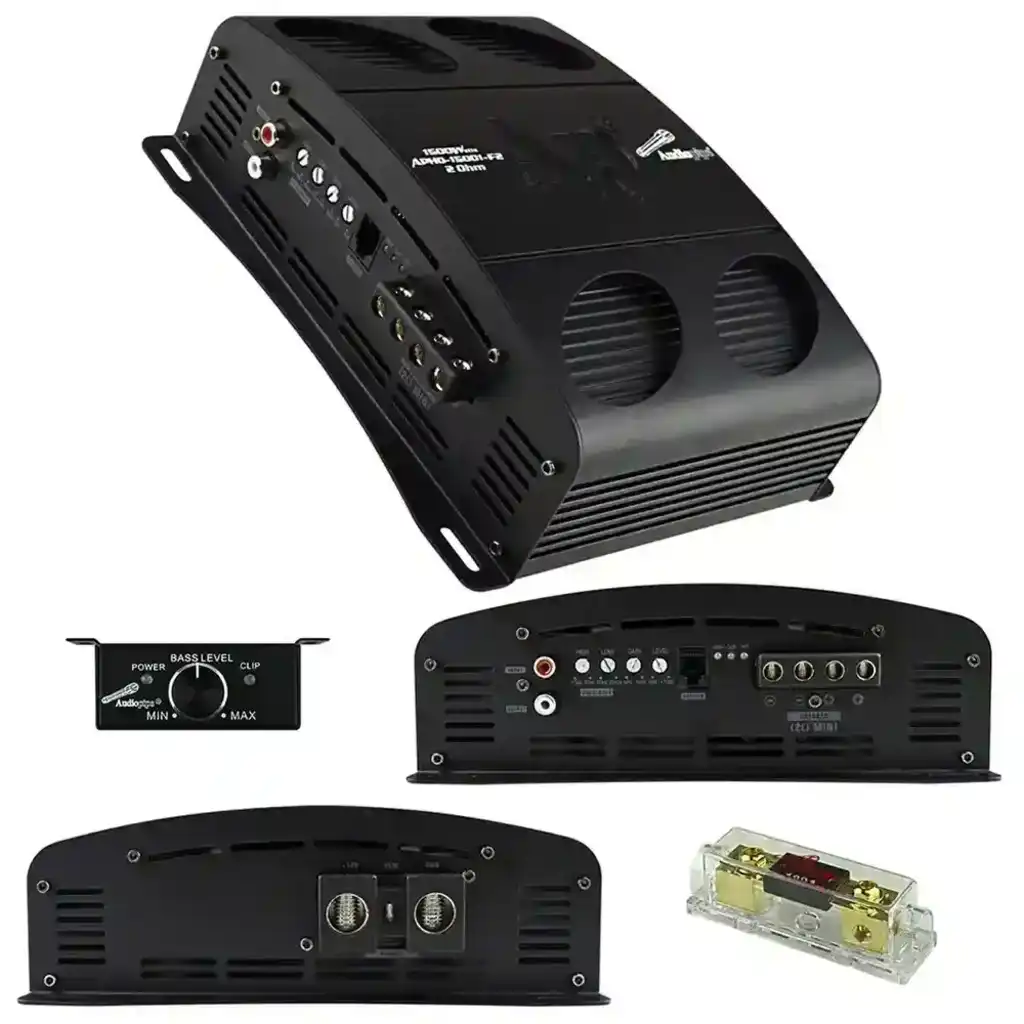
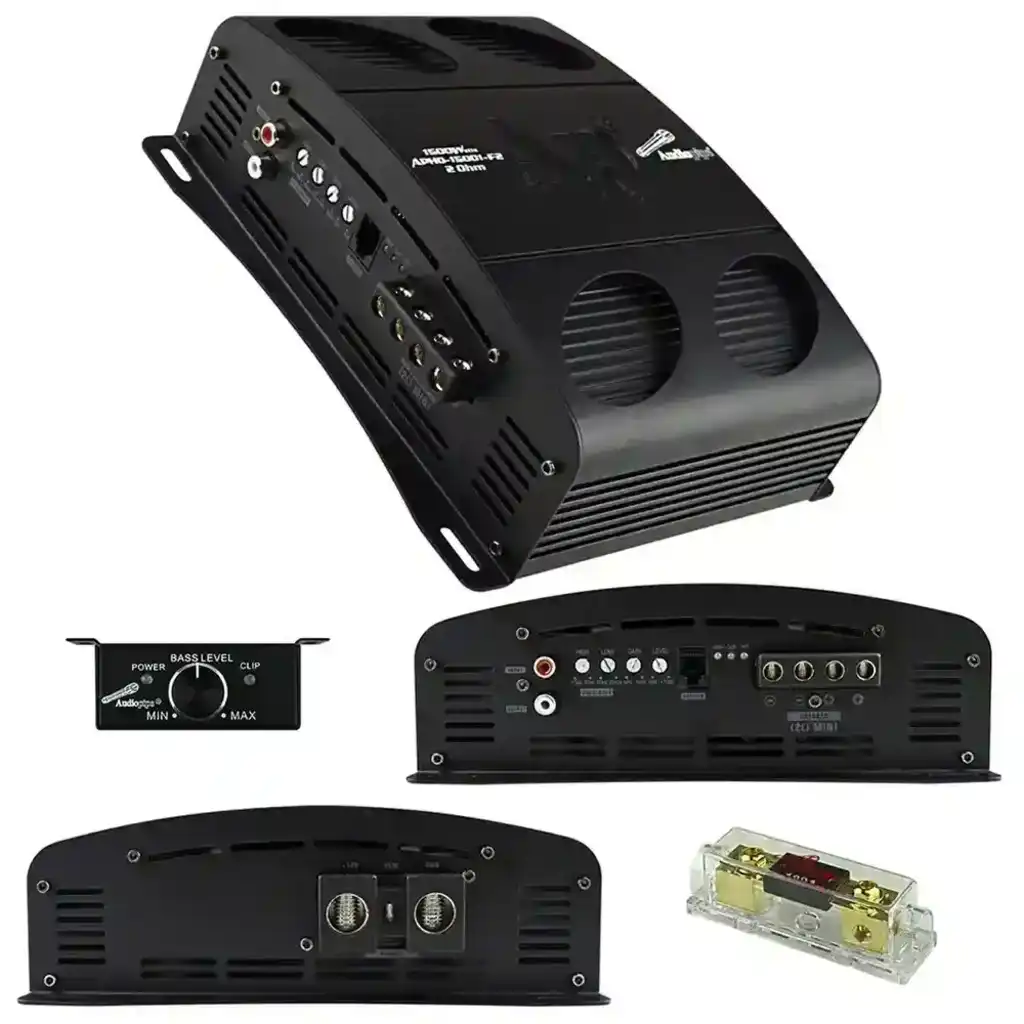
Full bridge Class D amplifiers are commonly used in professional audio equipment, high-power car audio systems, and other applications where high power output and efficiency are required.
Summary:A full bridge Class D amplifier is a highly efficient and powerful amplifier design that uses a full-bridge configuration to maximize output power while maintaining efficiency and sound quality. This makes it an ideal choice for high-power audio applications, particularly in scenarios where space and energy efficiency are important considerations.




Add New Comment